
A human has 46 chromosomes (a set of 23 you inherit from your mother, and a set of 23 from your father). Let’s try to tie all of this information together and see how it applies to chromosome and chromatid count during the various stages of cell replication.įirst, during the S phase of interphase, the genetic material of a cell is duplicated. Mammalian oocytes are arrested at prophase I until puberty when luteinizing hormone (LH) induces resumption of meiosis of follicle-enclosed. At the beginning of mitosis, for example, a chromosome consists of two sister chromatids – chromatids are the term used to describe the chromosome in its duplicated state. Cell Division Mitosis Reasons for Mitosis There are three main reasons growth repair/healing asexual reproduction Cell Division by mitosis Some cells divide. females have X chromosomes and males have Y chromosomes. diploid cells C The X and the Y chromosomes are called sex chromosomes because A. Chromosomes can exist in duplicated or unduplicated states. during metaphase of mitosis A In animals, somatic cells result from mitosis andresult from meiosis A. Chromosomes are an even denser packaging of chromatin that are visible with a light microscope, particularly during metaphase. However, during mitosis and meiosis, chromatin exists in an additional level of organization known as a chromosome. Throughout most of the cell cycle, DNA is packaged in the form of chromatin.
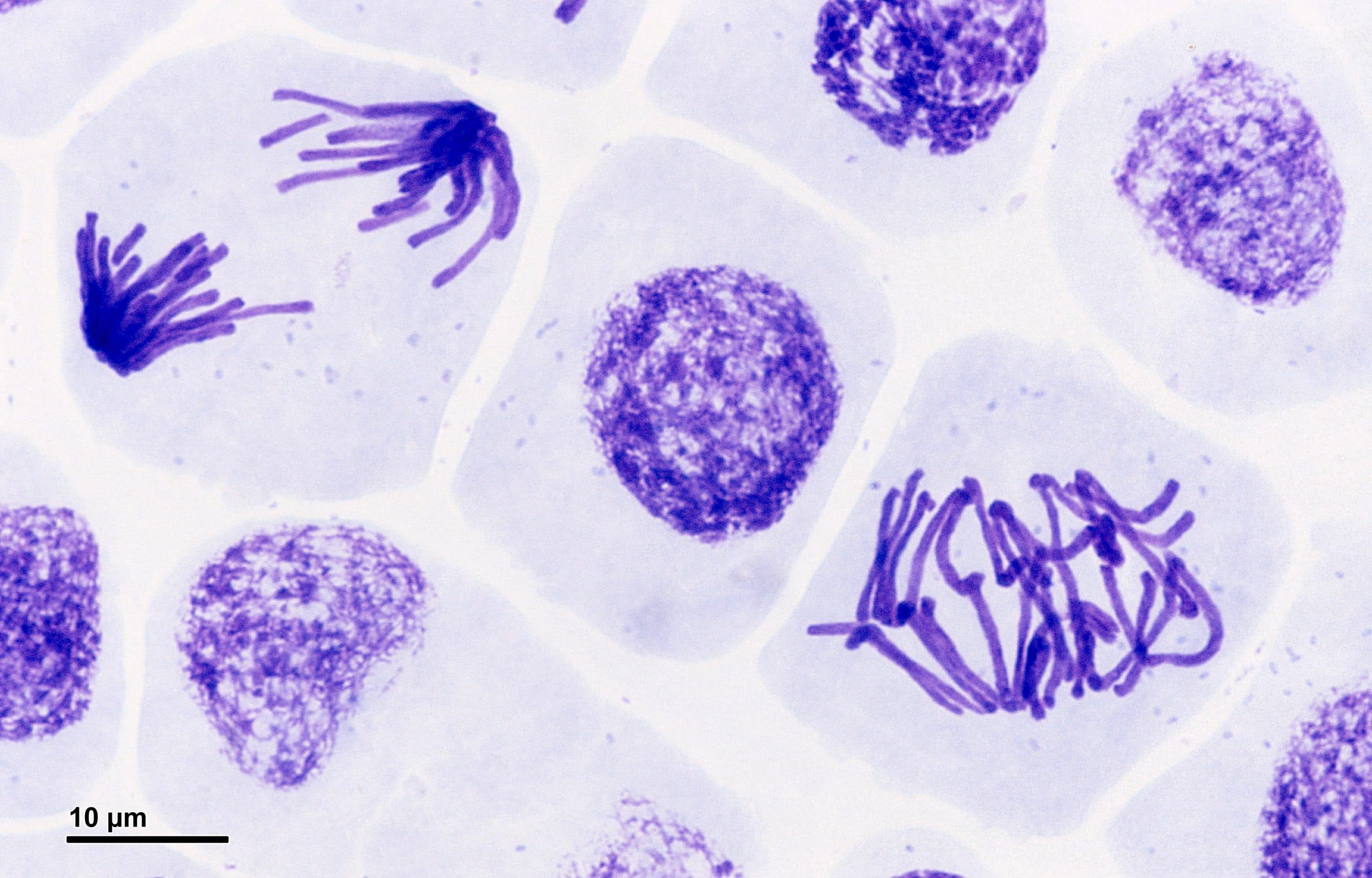
To first clarify this topic, it is first essential to understand some basic definitions.Ĭhromatin is the general packaging of DNA around histone proteins – this arrangement of DNA helps to condense DNA to fit within the nucleus of the cell. During the four phases of mitosis, nuclear division occurs in order for one cell to split into two. Additionally, we’ll mention three other intermediary stages (interphase, prometaphase, and cytokinesis) that play a role in mitosis.

A topic in biology that many students find challenging is the number of chromosomes and chromatids present during the various stages of meiosis and mitosis in eukaryotes. The four stages of mitosis are known as prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
